Dive into the Comparative DAG vs Blockchain debate to settle the score once and for all. As your tech guide, I’ll help you cut through the jargon and zero in on what really sets these two giants apart. We’ll tackle head-on the unique features that separate DAG, a new contender, from the established blockchain tech that’s been the backbone of crypto. Buckle in and let’s unravel this tech tangle together, keeping it simple and straight to the point from defining their fundamentals to dissecting their impact on the future. Get ready to explore how these platforms handle vast transactions and adapt to our digital demands without breaking a sweat—or the bank.
Understanding DAG and Blockchain Fundamentals
Defining Distributed Ledger Technologies
Let’s dive right into what makes these tech marvels tick. Distributed Ledger Technologies (DLT) are like a ledger, but spread out everywhere. On this ledger, you can see all transactions that ever happened. It’s like a huge shared diary, open for all to read!
Core Principles of DAG vs. Blockchain
Now, comparing DAG technology to Blockchain can be like talking about cats and dogs – both are great, but they’re different. Let’s break it down.
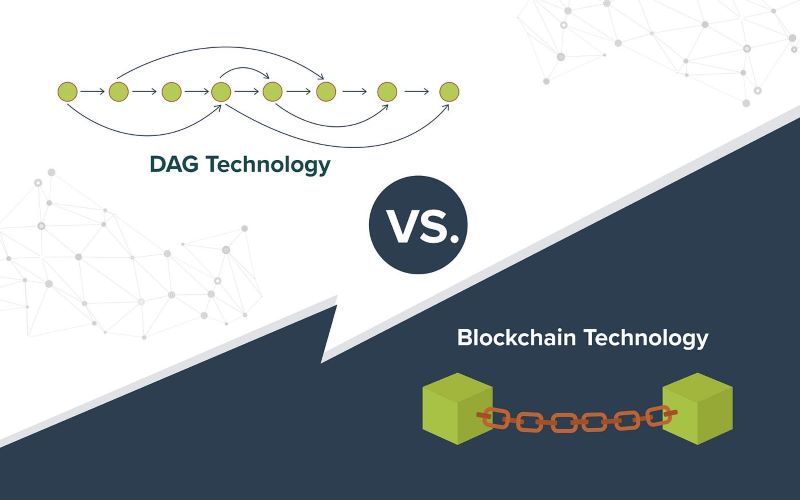
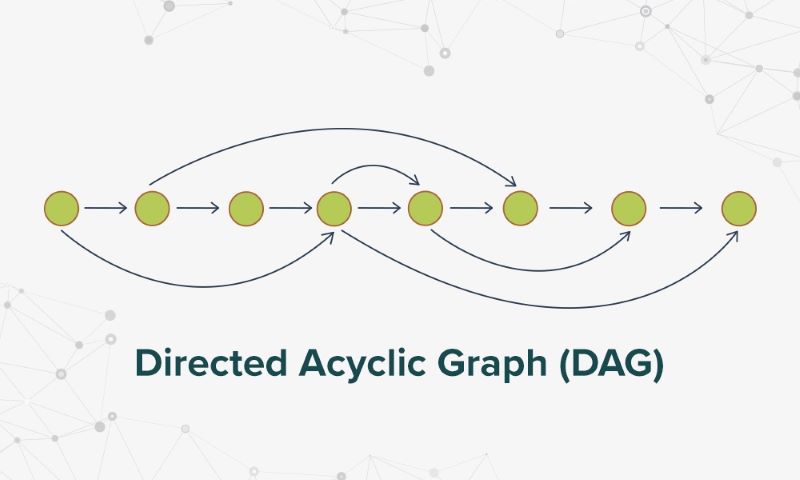
DAG stands for Directed Acyclic Graph. It’s a bit like a flow chart where every new piece of info helps confirm the last. This means you can have zero-fee transactions. Yes, you heard it right – zero! This is why DAG is great for handling transactions in the blink of an eye. Hence, when you think of buying a coffee with crypto, DAG might ring the cashier bell faster.
Blockchain, on the other hand, is a chain of info blocks linked with security in mind. Each block confirms the last, building a robust wall of data. It stands strong but can hit snags when many folks use it at once, leading to those infamous Blockchain scalability issues.
In terms of security, both systems bring their A-game to the table. Blockchain is like a fortress – hard to break into, with each block watched over by tough miners cracking complex codes. While DAG isn’t mined, it has its own clever ways to make sure each transaction fits like a puzzle piece, keeping the system clean and smooth.
On the decentralization front, Blockchain carries the torch high. Every miner’s vote counts when making decisions about the ledger. DAG’s approach is different. It may not have miners, but it does have network nodes working together to keep the ledger up-to-date, just in a slightly centralized fashion.
When it’s time to talk money, like transaction fees, Blockchain can get pricey when it’s busy. Picture a crowded market – the busier it gets, the more you might have to pay to get ahead. DAG swoops in with finesse, offering zero-fee transactions, which sure does sound like a sweet deal for your wallet and makes it ace for everyday use.
As for energy, Blockchain can be quite the energy hog. It’s got miners working round the clock, hungry for power. DAG stays light on its feet, needing much less juice to keep running.
In the world of crypto coins, DAG-based cryptocurrencies shine with speedy transactions while those built on Blockchain boast beefy security. IOTA’s Tangle is one cool cat in the DAG family, doing its own dance to process transactions fast and free.
Both DAG and Blockchain are like tools in a toolkit. One might fit better depending on the job. For mega companies, DAG slides in with solutions that work super fast. And when it’s about trusting a system with your assets, Blockchain stands sturdy.
Choosing between DAG and Blockchain might depend on your needs. Want lightning-fast speed without fees? DAG could be your hero. Need a vault-like space to keep your digital gold safe? Blockchain is here for you. And as we move into the future, who knows? We might just see these two join forces, taking on the digital world together.
Analyzing Performance: Scalability and Efficiency
Transaction Throughput in DAG and Blockchain Systems
When we talk about how many deals these systems can handle, we hit a big roadblock with blockchain. It can’t deal with a bunch of them at once. This is what I call a blockchain scalability issue. Imagine a checkout line that moves slower when more people join it. Not fun, right?
Now, Directed Acyclic Graph benefits shine here. This tech looks at transactions with fresh eyes. Each new transaction helps confirm others. This means the more action a DAG network sees, the faster it gets. It’s like having more cashiers open up as the store gets busy.
Network Efficiency – Analyzing Real-Time Capabilities
Efficiency is another playing field where DAG and blockchain duke it out. I’ve seen real-time transactions in DAG knock the socks off people who thought they knew fast. DAG-based cryptocurrencies, like IOTA’s Tangle, let data zip around without breaking a sweat.
Blockchain, on the other hand, can have you drumming your fingers waiting for confirmation. Mining in blockchain is like a complex dance that takes time to get just right. Security in these systems is strong, but boy, does it make you wait.
So while blockchain brings a lot to the table, it’s the agility and get-up-and-go of DAG tech that often grabs attention, especially for businesses that can’t afford to sit around and wait.
Sure, there’s no one-size-fits-all here. Both systems have their pros. But, when the rubber meets the road, it’s the zip and zap of DAG over the slow and steady of blockchain that could win the race.
Comparing Costs and Environmental Impact
Fee Structures Across DAG and Blockchain Platforms
Ever wonder how much it costs to send digital money? Well, it’s not about dollar signs. It’s about fees set by the network. In blockchain, every move costs you. That’s to pay the miners who keep things running. But in the world of DAG, it’s different. We often see low to no fees. That’s a big win if you’re tired of hefty charges.
Here’s a clear picture for you. Say you’re using Bitcoin, a popular blockchain currency. You pay a fee every time you send it to someone. This fee changes often and can get pricey. Now, in DAG, like with IOTA’s Tangle, you can send it for zero fees. That’s right, sending cash without the extra pinch.
Why does this matter? For one, lower fees make people happier to transact more often. They also make using cryptocurrencies for tiny purchases realistic. Imagine buying a coffee without a fee doubling its price. That’s what DAG tech aims to offer. To sum it up, DAG tries to keep your digital wallet heavier by cutting down those pesky fees.
Energy Consumption and Sustainable DLT Practices
Let’s talk about a hot topic: the power our digital money needs. Blockchain, especially Bitcoin, eats up a lot of energy. Why? It uses something called Proof of Work. Folks solve complex puzzles to validate transactions. And they use tons of computer power to do it.
On the flip side, DAG doesn’t rely on mining. Instead, it uses different methods to agree on transactions. This means a lot less energy used, way better for our planet.
Imagine a room full of roaring engines. That’s a bit like the blockchain’s energy use. Now picture a quiet library. That feels closer to a DAG’s energy vibes. A quieter, less energy-hungry space.
It gets real when we think long-term. The less energy we use, the less we harm our home, Earth. By choosing greener tech, like DAG, we play a part in saving our planet. We get to send and receive money while also going easy on nature.
So, back to the question of energy. Blockchain is like a big truck – strong but hungry for fuel. DAG is like a bike – it gets you there with way less fuss. The choice is clear if we want our future to be clean and green.
In the world of digital coins, this talk is central. Staying cool for the planet while doing our daily biz is no small thing. DAG’s light energy touch helps us do just that. It protects our pockets and our planet.
Fee structures and energy use are huge when picking the best digital money path. With DAG, we’re looking at a future that’s kind to wallets and the world. It’s a path that feels right as we stride into a clean, green future. So next time you think of sending a token, remember the costs. Not just to you, but to all of us.
Examining Use Cases and Future Prospects
DAG Integration with IoT and Enterprise Solutions
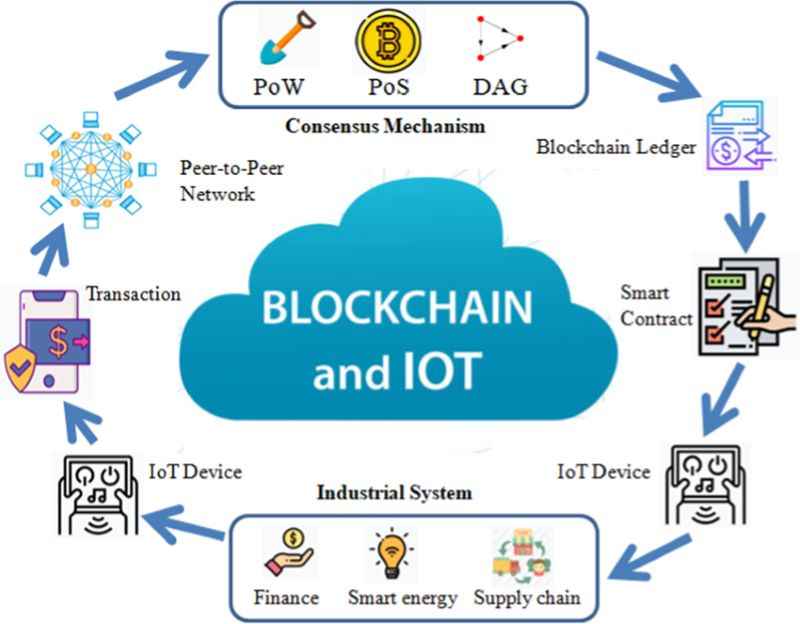
You’ve heard of Blockchain, right? But DAG is also a key player. DAG makes data sharing fast and easy, perfect for the Internet of Things (IoT). See, IoT devices love to talk to each other. DAG helps them chat without a wait.
Think of a smart home. Your fridge, oven, and lights need to communicate in real-time. DAG’s like their group chat. It keeps things smooth and quick. And for businesses, time is money. DAG steps in to track goods from factory to store, no delays.
Why does this work so well? DAG’s design has no miners to slow things down. Every user adds to the ledger, making the process faster. Factor in no fees, and it’s a win for businesses big and small.
What about security? With each new entry, the network gets stronger. So, hackers have a harder time breaking in. That’s why folks trust DAG for sensitive company data. The more it’s used, the more robust it becomes.
DAG technology also opens doors for new features. Things like voting systems and secure messages. Imagine voting from your phone with results ready in seconds! That’s the future with DAG.
Blockchain’s Role in Decentralization and Smart Contracts
Now, let’s talk Blockchain. Its superpower is decentralization. That means not one person or group controls it. This builds trust among users worldwide. With Blockchain, everyone sees the same ledger. So, it’s clear who owns what. This reduces fraud and builds confidence.
Smart contracts come into play here. Think of them as self-executing deals. When terms are met, the contract acts on its own. This is golden for businesses. It saves time and nixes the need for middlemen.
But here’s the rub. Blockchain has a tougher time with speed and costs. Each transaction needs miners for validation. This can slow things down when there’s a lot of activity. Also, with more users comes higher fees. That’s a bummer for those looking to save.
It’s not all slow-going, though. There are plans to make Blockchain faster and cheaper. People are looking into new rules, called consensus protocols, to help. But for now, Blockchain is still trying to catch up to DAG in that race.
Both DAG and Blockchain have their own shine. DAG’s fast and friendly for IoT and businesses. Blockchain is the king of keeping things in the open and secure. In the end, they both want to make sharing data safe and smooth. They just take different roads to get there.
The future? It’s something to watch. As DAG grows, it could change how we do everyday things. And as Blockchain improves, it could get speedier and lighter on the wallet. It’s a tech tangle, but boy, is it an exciting one!
We’ve traveled through the maze of DAG and blockchain in this post, cracking open the nuts and bolts of distributed ledger tech. We delved into how different they are at their core and saw just how these differences play out in real-world use.
When it comes to speed and getting more done, DAG takes the cake. It deals with transactions fast and doesn’t sweat when more action hits the system. Blockchain has its strengths, though. It’s the go-to for secure, smart contracts and spreading power across the board, unlike anything else out there.
Money talks, and so does how we treat our planet. We saw how DAG and blockchain stack up on costs and their hug (or harm) to mother Earth. With our world getting smarter and more connected, DAG’s buddy-buddy with IoT and big biz, while blockchain keeps changing the game with trust that’s spread far and wide.
Peeking at the future, it looks bright with these tech whizzes. DAG’s quick moves and blockchain’s trust magic are shaping a world that’s smarter and fairer for all. Stick with this ride, and you’ll see just how big of a deal these two giants are in the tech wonderland.
Q&A :
What are the main differences between DAG and Blockchain technologies?
DAG (Directed Acyclic Graph) and Blockchain are both types of distributed ledger technologies, but they differ in their structure and approach to processing transactions. While Blockchain organizes data in sequential blocks linked together, DAG allows for transactions to be linked in a graph that can flow in multiple directions and doesn’t require blocks. This leads to differences in scalability, speed, and consensus mechanisms.
How does the scalability of DAG compare to that of traditional blockchains?
DAGs are often touted for their scalability compared to traditional blockchains. Because DAGs do not require new transactions to be formed into a block and added to a single chain, they can process transactions in parallel, potentially leading to much higher throughput and lower transaction times as the network grows.
What are the advantages of using a DAG-based network over a Blockchain-based one?
One of the primary advantages of a DAG-based network is the potential for higher transaction throughput due to its ability to process transactions in parallel. This, in turn, can lead to lower transaction fees, as there is no need for miners to include transactions in a new block. Moreover, the structure of DAG allows for potentially faster transaction confirmations, which could be beneficial for applications requiring quick transaction finality.
Can a DAG-based system achieve the same level of security as Blockchain?
While DAGs offer several operational advantages, achieving the same level of security as a traditional Blockchain can be challenging. Because the consensus mechanism in a DAG-based system is not based on mining or staking in the same way as many Blockchains, it may use different algorithms to secure the network, which can vary in their robustness. Therefore, whether a DAG-based system achieves similar security to a Blockchain depends on its specific design and implementation.
Is DAG technology better suited for certain types of applications than Blockchain?
Yes, DAG technology may be better suited for applications that require high transaction throughput, microtransactions, or those that need transactions to be confirmed quickly. This can include IoT applications, micro-payment platforms, and certain financial services. Blockchain, on the other hand, may be preferred for applications that prioritize security and decentralization over transaction speed, such as those handling large value transfers or record-keeping.