Diving into basic technical analysis for beginners can turn baffling market patterns into clear signals. Ever stared at a stock chart, felt your eyes glaze over, and wondered what on Earth you’re looking at? You’re not alone. Charts and graphs can look like a wild code only the pros can crack. But guess what? You can crack it too, and I’m here to hand you the decoder ring. Starting with the building blocks of stock charts and the secrets in candlestick shadows, we’ll journey through the maze of trend lines and price whispers. Next, we’re going to tackle the game of financial tug-of-war with support and resistance levels. Armed with simple moving averages, you’ll gain the foresight of a market oracle. From the fast-paced buzz of RSI and MACD to the rhythm of market heartbeats through volume and Bollinger Bands, these tools are your trading GPS. By the end, you’ll be drafting up a trading plan that’s both sturdy and nimble, ready to take on the daily dance of digits. Let’s unravel these market mysteries together.
Understanding the Basics of Stock Charts
The Significance of Candlestick Patterns
If you’re new to stock trading, you first need to get a handle on candlestick patterns. Think of each candlestick as a snapshot of a stock’s price war between buyers and sellers. Each candle has two parts—a body and wicks. The body shows where the price opened and closed. The wicks or ‘shadows’ show the high and low points.
These patterns can tell you a lot! For starters, they may hint at where prices might go next. Spot a candle with a small body and long wicks? That’s ‘indecision’ in trader speak. It means neither buyers nor sellers have the upper hand. See a long green (or white) body? Buyers are winning, and the price might keep rising.
Now, say you’re scanning a stock chart, and you come across a line-up of candles that looks like a small army marching up the chart. That’s a ‘bullish’ pattern, a sign prices might continue to climb. On the flip side, if the candles look like they took a dive off a cliff? Watch out, that’s a ‘bearish’ setup, and prices might keep falling.
Learning candlestick patterns can seem like learning a new language. But once you get the hang of it, it’s like having a secret window into the market’s mood swings. Beginners should start with basics like the ‘hammer’ for reversals and ‘engulfing’ for momentum.
Navigating Through Trend Lines and Price Movements
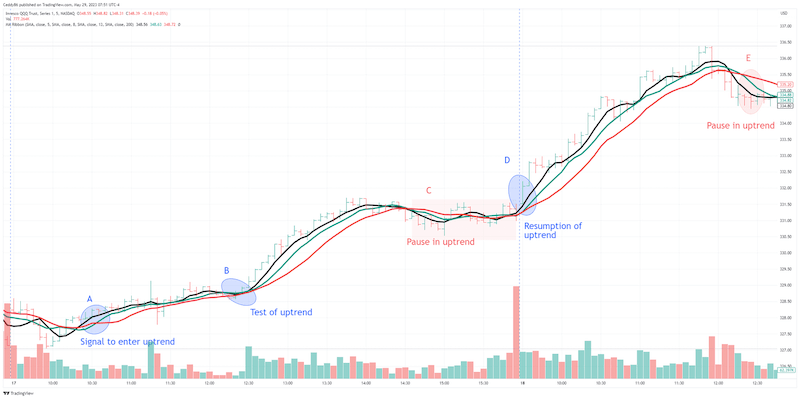
Now let’s talk trend lines. You see lines everywhere in life, and in trading, they’re just as important. Trend lines connect the dots of a stock’s price highs or lows. They help us see where support and resistance levels are. These levels are like invisible barriers where prices tend to change their minds.
Drawing trend lines on your stock chart is like adding guardrails to a winding road. They guide your eyes and help you spot where the price might bounce back or break through. When a price crosses a trend line, get ready. It could signal a big move is coming.
Say you’re looking at a stock, and it keeps bouncing off the same price floor. That’s ‘support.’ It’s like a trusty floor that keeps the price from falling through. On the other hand, if the stock can’t seem to break through a ceiling, that’s ‘resistance.’ It’s keeping the price from soaring higher.
But here’s a pro tip: the more times a price tests these levels without breaking them, the more ‘significant’ they become. If they do break, expect a big move—a breakout. And when old resistance becomes new support (or vice versa), that’s where trend lines really shine.
In short, start by watching how candles form patterns and how price dances around trend lines. Practice these basics to unlock market mysteries. And remember, keep it simple when you start. You’ll be spotting winning opportunities soon enough.
Remember, it’s a mix of practice and patience that’ll turn you from a newbie into a savvy reader of the stock market’s stories.
Mastering Support and Resistance
Identifying Key Levels for Entry and Exit Points
To win at trading, you need to know when to enter and leave. Think of it like a game. You have to know the good spots. These spots are support and resistance levels. Now, you might wonder, “What exactly are support and resistance levels?” Support is like a floor that holds the price of a stock up. Resistance is like a ceiling that keeps it from going higher.
When stock prices drop, they often stop and bounce back up at the support level. But if a stock climbs up, it might hit the resistance level and fall again. You want to buy near support and sell near resistance. That’s how you make money in trading. By finding where these levels are, you understand stock charts better.
Now, let’s talk about how you learn these levels. You look at stock market graphs. You find the spots where prices stopped falling or climbing many times. They’re clues to where support and resistance are. Beginning traders, watch these spots. They tell you when to jump in or out of the market. Keep an eye on them, and you’ll learn technical chart analysis in no time.
Implementing Moving Averages in Your Strategy
Moving averages are like magic wands for your charts. They smooth out price data so you can see the trend easier. For starters, a moving average is just an average of stock prices over a set time. When prices go above the moving average, think about buying. If they drop below, think about selling.
There are two types we focus on: simple (SMA) and exponential (EMA). SMA is like a slow, steady friend. It’s good for seeing long-term trends. EMA is quicker, more about what’s happening now. It reacts faster to price changes, which is great for you newbies who want in on the action. By using these averages, you can catch trends early. This gives you a head start.
Let’s break it down. Use a simple moving average strategy if you want a broad look. If you’re going to know what’s happening right now, use EMA. Both are tools that help beginners understand moving averages for newbies. Don’t worry about the hard stuff. Start with these basics, and you’ll be good to go.
In summary, getting to know support and resistance can change your trading game. And once you add moving averages to your toolkit, you’ll be reading market indicators like a pro. The market can seem big and scary, but with these tools, you’re well on your way to cracking its code. Keep practicing, and remember, learning to read stock charts is your key to success.
Utilizing Leading and Lagging Indicators
Reading Market Sentiment with RSI and MACD
When you’re new to the stock market, it seems like a web. It can feel like you’re trying to read a message in a bottle that’s bobbing in the middle of the ocean. But fear not, with the right tools, you can begin to make sense of it all.
A key tool in your kit should be the RSI, or Relative Strength Index. Think of it as the market’s heartbeat monitor. It tells you if stocks are weak or strong. If RSI is over 70, it’s like the market just had a sprint and might need a rest. If it’s under 30, the market might have been sitting too long and could be ready to jump up.
The MACD, or Moving Average Convergence Divergence, is your market weather vane. It shows if a storm is coming or if clear skies are ahead. When the MACD line crosses above the signal line, it’s usually a sunny day for stocks, a good time to buy. When it dips below, it might be time to pack up and go home.
Volume Indicators and Bollinger Bands: Timing Your Trades
Now, let’s talk about volume. Volume indicators are like your trading concert speakers. They let you hear if the stock’s music is loud or soft. A loud volume often means a big move is coming. A soft volume? The market might just be humming along.
Bollinger Bands are like the ropes in a ring. They help you see if a stock is at one extreme or another. If it’s at the outer band, it could be time for it to bounce back to the middle. If it’s near the middle band, it might stay on course or switch direction.
Learning to play with these tools takes some practice. For novices wanting to learn technical chart analysis, start small. Watch how RSI and MACD move through the day. Keep an eye on your volume. Check where stocks are between their Bollinger Bands. Over time, patterns emerge like footprints on a trail. And once you learn to spot them, you’ll find it’s not a web at all – it’s a map to potential treasure.
Just remember, all these gadgets are not crystal balls. They guide us but can’t predict every market move. It’s like the weather again: you know what to dress for but sometimes get caught in the rain. Don’t be discouraged. The key is to watch, learn, and, most importantly, stay patient. It’s all part of the journey in trading.
Analyzing market sentiment can often make the difference between a good and a great trade. Tools like RSI and MACD give you a peek into the market’s mood. Volume tells you about the market’s passion, and Bollinger Bands show the market’s boundaries. Use these, and you’ll have a strong foundation for technical analysis. With practice, you’ll read stock charts like a pro, time your trades better, and hopefully, capture more gains in your own exciting journey through the stock market. Welcome to the hunt!
Developing a Solid Trading Plan
Recognizing Chart Patterns for Effective Trade Setups
Let’s dive straight into chart patterns. These are key to setting up trades. They look like shapes within stock charts. They hint at where prices might go next. Think of them as secret signs. They unlock stock market mysteries. Learn these and you’ve got a treasure map for trading.
Patterns include things like ‘head and shoulders’ or ‘triangles.’ When you see a ‘head and shoulders,’ it means a stock price might drop. ‘Triangles’ can signal a big price move, up or down, is on its way. Spotting these early helps you plan when to buy or sell.
Differentiating Between Day Trading and Swing Trading Practices
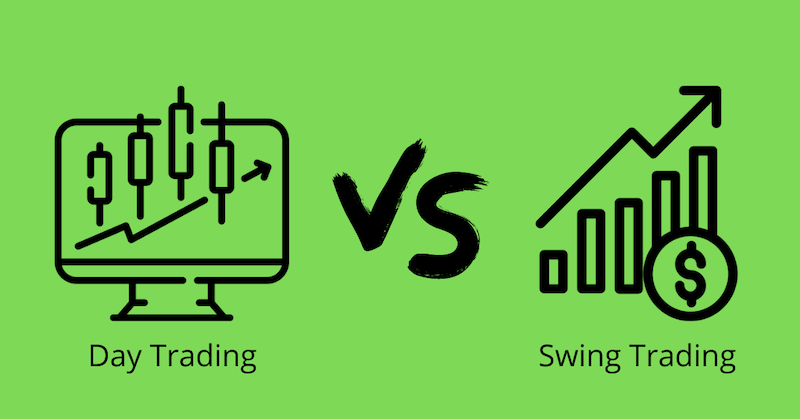
Now, day trading versus swing trading – what’s the difference? Day trading is like a fast game. You buy and sell stocks all in one day. Think quick moves and quicker profits. But, it can be risky. Prices can change in seconds. You need sharp eyes and a clear plan.
Swing trading is a bit slower. You hold stocks for days or weeks. It’s like waiting for the perfect wave to surf. It requires patience. You study the stock’s pattern to predict the next big rise or fall. Swing trading lets you take a breath and plan more.
Remember, practice makes perfect. So, start small and learn from each trade. Use these tips and soon you’ll read charts like a pro!
We’ve dug deep into stock charts, a key tool for smart trading. From candlestick patterns that give quick clues, to trend lines that show price paths, getting these basics can make a huge difference. We then tackled support and resistance, the ‘do not cross’ lines of trading. Knowing where to jump in or out is gold, and those moving averages? They’re your trusty guides in a choppy market sea.
We didn’t stop there. We got our hands on those secret signals—RSI, MACD, volume hints, and those snug Bollinger Bands. They’re not just fancy names; they’re your front-row seats to market moods. Last but not least, we mapped out a solid trading plan. Spotting chart patterns sets you up right, and choosing between day or swing trading can make or break your game.
So what’s my final nugget of wisdom? Master these skills. The market’s a wild ride, and these tools are your best shot at riding high in trading. With practice, patience, and these strategies, you’re ready to take on the stocks like a pro. Go for it!
Q&A :
What is basic technical analysis and how can beginners start using it?
Technical analysis is a method of evaluating and predicting the future price movements of a financial asset, like stocks, commodities, or currencies, by analyzing past market data, primarily price and volume. Beginners can start by familiarizing themselves with fundamental concepts such as support and resistance levels, trend lines, and moving averages. It’s important to start with a clear understanding of the market they wish to analyze and to practice on simulators before trading real money.
What are the key principles of technical analysis that every beginner should know?
There are several key principles in technical analysis that novices should be aware of. Firstly, ‘price discounts everything’ which means that all information—economic, political, or otherwise—is already reflected in the market price. The second principle is that prices move in trends and it’s generally easier to predict the future price movement within a trend than to predict a new trend. Lastly, history tends to repeat itself, as market psychology is driven by human emotions like greed and fear that are predictable and reflected in patterns on price charts.
Can beginners rely solely on technical analysis for making trading decisions?
While technical analysis can be a powerful tool for forecasting market trends, beginners should not rely solely on this method. Combining technical analysis with fundamental analysis, which examines economic indicators, company financials, and other qualitative and quantitative factors, provides a more holistic approach to trading. Furthermore, risk management and emotional control are also critical for success in trading.
What are some common technical analysis tools and indicators for beginners?
Beginners should start with easy-to-understand tools and indicators such as:
- Candlestick charts: to recognize patterns that indicate potential price movements.
- Moving averages: to identify the direction of the trend.
- Support and resistance levels: to identify where prices might change direction.
- Volume: to measure strength or weakness of a price trend.
- Relative Strength Index (RSI): to assess whether an asset is overbought or oversold.
Understanding and using these tools can give beginners a good foundation in technical analysis.
How much time do beginners need to spend learning technical analysis before they can effectively apply it?
The amount of time required to learn technical analysis can vary greatly from beginner to beginner. It depends on individual learning pace, the complexity of the concepts, and the time devoted to practice and study. Many may start to grasp the basics within a few weeks, while proficiency could take several months to a year. Continuous learning and real-time practice are essential for effectively applying technical analysis.