Imagine a world where everyone agrees with a nod. That’s what Types of consensus mechanisms in blockchain do – they’re the nodding heads of the digital realm. These mechanisms are the backbone that keeps all users on the same page. Forget one-size-fits-all; blockchain has a tailored fit for every need. When I guide you through this maze of options, you’ll see how these systems make or break the trust in a network. We’ll dive into the original go-to, called Proof of Work, and why some are shifting to a newcomer, Proof of Stake. By the time we’re done, you’ll grasp how these choices touch everything from power bills to how much you earn by just taking part. Join me in peeling back the layers of blockchain’s cooperative core.
Exploring the Landscape of Blockchain Consensus Mechanisms
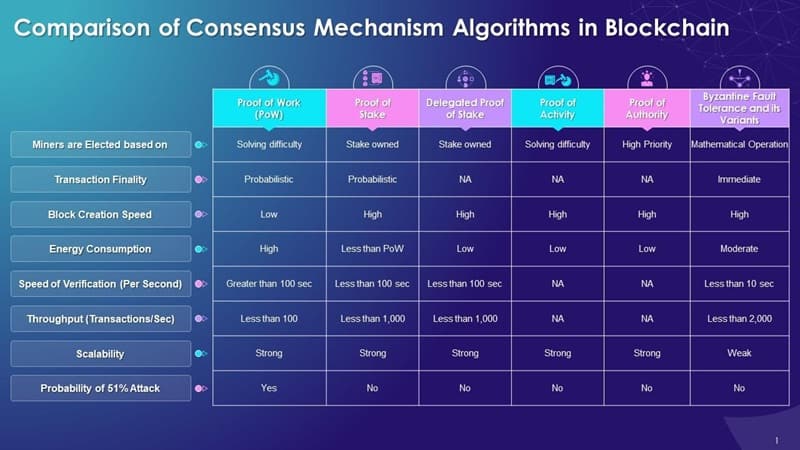
Understanding the Basics of Proof of Work (PoW)
Proof of Work makes our blockchains safe. Think of it like a math puzzle. To add a block, you solve it first. It’s proof you did the work. This keeps our digital money safe from cheaters.
Mining is key here. Miners solve puzzles using powerful computers. This process makes new coins and checks transactions. But it needs a lot of power, which can harm our planet due to high energy use.
High hash rates mean strong security. In PoW, a high hash rate keeps the network from attack. It means many miners check and secure our transactions.
Proof of Work is the first way we made sure everyone agreed on what’s in the blockchain. It works well but needs lots of energy. Because of this, some people started to look for new options that use less power.
The Shift Toward Proof of Stake (PoS)
Proof of Stake is a new way to keep our digital money safe. With PoS, you don’t mine, you stake. You lock up some of your coins to get a chance to make a new block. The more you stake, the better your chances.
This way uses less energy. Instead of math puzzles, it uses your staked coins as proof. This helps save our planet by cutting down energy use.
Block producer selection in PoS happens by how much you stake. More staked coins mean more trust. So, you get a better shot at making a block.
Validator node requirements in PoS are different from mining. You don’t need big computers. You just need to own coins and be part of the network.
People like PoS since it’s not as hard on our environment. It lets more people join in, as you don’t need big machines. You just need to have some coins to stake.
In PoS, staking your coins gets you rewards. When you stake and your computer helps the network, you earn more coins. This is like getting interest on money in a bank.
A big question is which one is better. PoW has been around longer, but PoS might be better for our planet. Both have bright minds working to make them even better.
As you see, blockchains stay truthful to their records through these consensus mechanisms. Whether it’s PoW, with its energy-hungry math puzzles, or PoS, with its eco-friendly coin staking. Both aim to keep our digital trade fair and safe.
Now you know how our digital money stays in check. It’s all about people agreeing which blocks to add to the blockchain. And as our digital world grows, the way we all agree will keep getting smarter.
Choosing which method to use is a big deal. It affects how we all trust and take part in this new digital money world. This makes our talk about PoW and PoS super important. It’s how we make sure our future with crypto is bright and fair for all.
The Shift in Efficiency and Security: PoW vs. PoS
Evaluating PoW and PoS in Energy Consumption
Look at your light bulb. It uses energy. Blockchains do too. They’re like digital ledgers. Think of them as big books full of info on who sent what to whom. To keep this book safe and correct, blockchains use special rules. We call these rules consensus protocols. They help everyone agree on what’s in the book.
Let’s talk about two big ones: Proof of Work (PoW) and Proof of Stake (PoS). You’ve heard of Bitcoin, right? That’s PoW. It makes computers solve puzzles to add new pages to the book. These puzzles need lots of energy, like a ton per puzzle. Imagine every computer in a huge city just working on one puzzle. That’s PoW-level energy!
Now enter PoS. It’s like saying, “Hey, I’ve got some coins. I promise not to cheat.” If you cheat, you lose them. Simple, yeah? So, instead of puzzles, it’s like a lottery based on how many coins you hold. More coins? Better chances. It uses way less energy. Imagine just a single light bulb for the room. Much better, huh?
Looking at energy use, PoS wins. It’s like riding a bike vs. flying a jet. PoS is the bike – good for your health and the planet.
Analyzing Security Differences Between PoW and PoS
Now, let’s chat about safety. These protocols are like guards for our digital ledger. PoW has tough guards. They make sure no one is lying about the transactions. The thing is, these guards need a lot of muscle (energy) to do their job. To mess with PoW, you’d need more muscle than half the guards combined. That’s rare and costly, so PoW ledgers—pretty safe.
Next up – PoS. Its guards are the people with coins. If they mess up, they lose their coins. See the twist? You put your own money on the line. You’re less likely to gamble your money on a bad move. That’s what makes PoS secure. But if someone has loads of coins, they have loads of power. That can be risky if they turn into bullies.
Both PoW and PoS have strong walls. PoW’s wall is built with energy bricks. PoS’s wall is built with trust bricks. Your pick depends on what you value: energy or trust?
In the end, who wins in safety? It’s a close call. PoW is like having a bodyguard who eats a lot. PoS is like a group of friends watching your back. Good friends won’t let you down, but it’s hard to find a good bodyguard. Both keep you safe, just in different ways.
Each ledger writer (we call them miners in PoW, validators in PoS) has a rulebook. It tells them how to write in the ledger. It’s super important. It stops cheats and helps trust.
So, we’ve poked around energy and safety in these blockchain rulebooks. PoW uses a lot more juice but has a track record. PoS is lighter but newer. Choosing between them is about what costs more to you – watts or trust?
The Stakeholders in Blockchain Governance
The Role of Validators and Their Node Requirements
Who keeps a blockchain trusty and tight? Validators! They make sure each block locks in right. Validators are blockchain champs who play fair. They check if all dealings are square and on the up. Their computers, called nodes, need to be tough and always on. They need a good net hook-up to stay in the know. Big blockchains ask for nodes with more zip. They need fast brains and lots of digital room.
Validators guard the blockchain day and night. Bits and bytes zip round the globe, as their nodes stay alert. They use key codes to vote, saying “yes” or “no” on new blocks. Their vote seals the deal on what’s true in the chain. Nodes chat using smart rules to keep in sync. These rules make sure all nodes agree on what’s what.
These blockchain heroes need some skin in the game. They bet their own coin that they’ll stay true blue.
The Economic Implications and Rewards of Staking
Now, what’s in it for these blockchain watchers? Staking! It’s like laying down your chips, betting on being a straight shooter. You lock up some coin, and if your node acts right, you earn more. It’s like getting a thank you for doing a solid job.
But it’s not just a pat on the back. Staking can pay off, like a little money tree. If your node helps lock in legit deals, you get a slice of the fees. More blocks nailed down means more coin in your pocket. Plus, staking keeps the whole chain on the level. With lots of folks with coin on the line, folks can bet the chain stays pure as gold.
Validators on the blockchain don’t just sit tight. They keep the ledger straight and earn their keep, fair and square. They put their own stash on the line to help every transaction stick. They are the unseen hands that keep your digital gold safe. Without them, the blockchain would be just a wild west of bits and bytes. Staking is not just a game; it’s the lifeblood of blockchain trust.
The Future of Blockchain Consensus: Sustainability and Scalability
Addressing the Environmental Impact of Consensus Methods
Blockchains need a way to agree on data. Proof of work has been the go-to. It makes computers solve hard puzzles to add blocks to the blockchain. This uses a lot of energy. Think of a small country’s worth. Not good for our planet, right?
Proof of stake comes to save the day. It picks block creators based on how many coins they hold and are willing to “lock up” as security, which uses much less power. This helps the environment because less energy means fewer greenhouse gases. It’s like replacing old, energy-guzzling bulbs with LEDs. Each one of us doing a small part makes a big difference.
To compare PoW with PoS, imagine two schools. One tests students with tough exams, needing lots of study nights. That’s PoW. The other picks class helpers based on good behavior points. That’s PoS. The second school is like a breath of fresh air, quite literally.
Tackling Scalability Through Advanced Consensus Protocols
Now, let’s talk about handling loads of transactions. More people are using blockchains, which means more transactions. Scalability is key. A blockchain that can’t handle growth is like a truck on a small lane, creating a big jam.
Think of delegated proof of stake (DPoS). Here, coin holders vote for a few to manage the blockchain. It’s like picking a class president. This speeds things up like when you have one person taking notes in a meeting rather than everyone talking over each other.
Then there’s practical Byzantine fault tolerance. It’s a mouthful, yes, but it means even if some nodes are bad, the network still agrees on the data. It’s like having a solid plan B when plan A hits the fan.
Improving these methods helps scale up nicely. It’s like adding lanes to that busy road. More cars, or in this case, transactions, can move smoothly. Everyone’s happy, and no one’s late for dinner.
New tech keeps showing up, with different ways for nodes to talk and agree. Some use less energy, some are super fast, and some do both. Remember, no wasted energy is step one for a greener planet, and moving lots of data without a hiccup is what we all want.
Start building a better future for blockchains, today. The key? Look at the tech you choose like picking a new car. Go electric, go efficient, and make sure it can handle a road trip without breaking down.
We dove deep into blockchain’s heart to see how it ticks. We looked at Proof of Work and how tough it is on the planet. Proof of Stake came next, with its lighter touch on Earth and new ways for folks to take part. We found that keeping these systems safe and running well comes with big costs and rewards. Our trip ends with a peek at what’s ahead. Better for the Earth, fitting more on the block train, these are big deals.
I’m not just tossing words around – this stuff matters. Big energy use and online safety are no joke. How we pick who watches over the block party is key too. We need smart plans that don’t hurt our world and still let block chains grow.
Blockchain is shaping up, getting ready for a future where it can do more without costing so much or being risky. That’s a win for everyone. With every step, we get closer to block chains that are good for wallets, good for keeping stuff safe, and even good for our planet. Let’s watch this space – it’s going places.
Q&A :
What Are the Different Types of Consensus Mechanisms Used in Blockchains?
In the blockchain world, consensus mechanisms ensure that all participants agree to the validity of transactions. The most popular types include Proof of Work (PoW), Proof of Stake (PoS), Delegated Proof of Stake (DPoS), and Proof of Authority (PoA). Each has unique attributes that make them suitable for different kinds of blockchain networks.
How Does Proof of Work (PoW) Ensure Blockchain Security?
Proof of Work, used by Bitcoin, requires participants to solve complex mathematical puzzles to validate transactions and create new blocks. This process requires substantial computational power, deterring malicious actors by making attacks economically unfeasible. The intensive nature of PoW also acts as a mechanism to control the creation of new blocks.
What Makes Proof of Stake (PoS) a Preferred Consensus Mechanism?
Proof of Stake is favored for its energy efficiency compared to PoW. Instead of mining, validators are chosen to create blocks based on the number of coins they hold and are willing to “stake” as collateral. It encourages holding coins over time, providing a potentially more scalable and eco-friendly alternative to PoW.
Can Delegated Proof of Stake (DPoS) Improve Transaction Speeds?
Yes, Delegated Proof of Stake aims to enhance transaction speeds and scalability. In DPoS, token holders elect a limited number of delegates to validate transactions and produce blocks. This reduced number of validators speeds up the consensus process and can handle a higher transaction throughput.
What is Proof of Authority (PoA) and Where is it Most Applicable?
Proof of Authority is a consensus mechanism where transactions and blocks are validated by approved accounts, known as validators. It’s typically used in permissioned blockchain networks where trust is placed in these validators due to their reputation and credibility. PoA is most applicable in situations where high throughput and fast consensus are required, without the need for a trustless environment.
By incorporating relevant keywords and providing valuable content, these FAQs are optimized to cater to searchers looking for information on consensus mechanisms in blockchain, aiming to improve search visibility and authority on the topic.