Unveiling the Blocks: What Is a Layer 1 Blockchain Revealed
Block by block, the digital world is shaking with the raw power of layer 1 blockchains. They are the bedrock, the original powerhouse of the crypto realm. When we talk about blockchain, these are the giants upon whose shoulders every other technology stands. What is a layer 1 blockchain, you ask? Picture a sprawling city with its own rules, currency, and land, but this city is digital and its foundations are unbreakable, decentralized ledgers. These are the base layers where crypto magic begins and where every transaction is a part of history. From Bitcoin’s grand draft to Ethereum’s crafty smart contracts, they’re the base protocols that make or break the crypto universe. Stay tuned, and I’ll unwrap this digital enigma, folding out each layer to reveal the strength and brains beneath these crypto titans.
The Foundations of Layer 1 Blockchain Technology
Understanding Base Protocols and Infrastructure
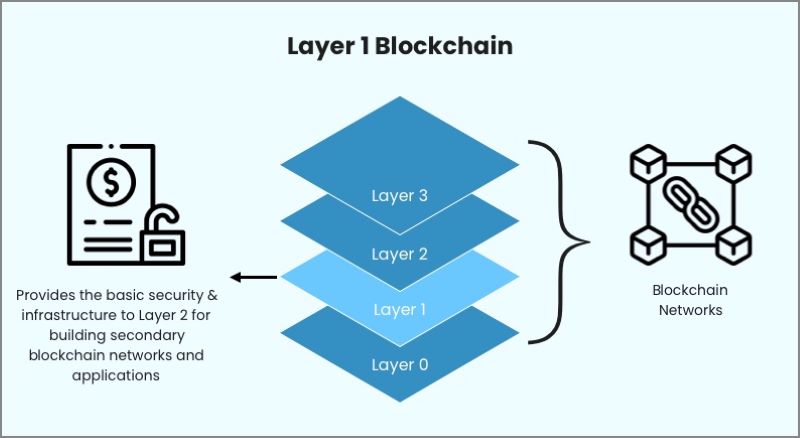
A layer 1 blockchain is the main network. It is where all the crypto action starts. It records all transactions and stores them. The technology behind it supports the whole system. Big blockchain names like Bitcoin and Ethereum are layer 1 blockchains. They each have a set of rules called a base protocol. This protocol sets how data is stored and kept safe.
These base protocols are key. They form the blockchain infrastructure. Think of it as the roads and bridges for data in the blockchain. It’s built to be tough. This makes sure that the data is always correct and safe.
The blockchain foundation technology is just like the concrete for these roads and bridges. It’s the bedrock for a safe and solid system. We can trust it because it’s well made. The primary blockchain layer is like the main highway. All other smaller networks connect back to it.
This layer is where the fundamental blockchain network lives. It has to be strong to handle lots of data. Think of it like a big market. Many people come and go, making deals all the time.
Deciphering Consensus: Proof of Work vs. Proof of Stake
Now, let’s talk about blockchain consensus mechanisms. Consensus means agreeing on something. Blockchain uses this to keep everyone on the same page. Two main types are Proof of Work (PoW) and Proof of Stake (PoS).
Proof of Work is the old way. It’s like a huge math contest. Computers race to solve tough puzzles. The first one to solve it gets to add a block of transactions to the chain. This method is used by the Bitcoin network.
Proof of Stake is newer and different. People lock up some of their digital coins to get a chance to add a block. This is called staking. If they’re picked, they check the new block and make sure it’s good. This uses less power and is faster.
Both ways help to keep the decentralized network safe. They make sure no one cheats. Security is tight, which builds trust.
So, Proof of Work needs lots of power but is time-tested. Proof of Stake is more about trust in how much you hold. Both are important. They help layer 1 blockchains work and keep them secure. This is what keeps your cryptocurrency safe.
The Core Components of Layer 1 Blockchains
On-Chain Transactions and Smart Contract Integrations
Layer 1 blockchain is like the ground floor of a building. It’s where everything starts. Here, data lives on one shared ledger. It means all info is ‘on-chain’. This is different from ‘off-chain’, like a side deal not on the books. It’s important because layer 1 is the base. Think of it as the sturdy foundation for a house.
On this ground floor, we have smart contracts. They are like digital promises. When set rules are met, the smart contract self-executes. No need for a middleman. This is like a vending machine giving snacks when you pay. This tech lets people trust the system. It makes deals safe and quick.
The beauty here is in its simplicity. On-chain actions are traceable, safe, and set in digital stone. No one can mess with them once done. This builds trust in the blockchain. People can deal directly without worry. No cheats, no takesy-backsies.
The Role of Cryptocurrency Native Tokens and Governance
Now, let’s chat on native tokens and who’s the boss. Every blockchain’s got its own money, or ‘cryptocurrency native tokens’. Think of them like arcade tokens, but for blockchains. They’re not just for buying stuff. They help run the system too.
So who makes the rules? That’s where ‘blockchain governance’ comes in. It’s like a school’s rules, decided by votes. Token holders get a say. More tokens may mean more votes. It’s how changes are made and choices picked. Fair and square, everyone’s voice counts.
This is key to keep things smooth. Like teachers in a school, governance sets who can do what. It keeps everyone on track, tweaking rules as needed. These rules help blockchains stay alive and kicking. With them, layer 1 blockchains can handle more action over time without a hitch.
Big words aside, it’s all about people getting along. Native tokens and governance make sure of that. They’re the heart and soul of this digital world. Keeping it fair, safe, and always running.
So, that’s the scoop on on-chain transactions and their buddy smart contracts. Plus, a dive into native tokens and those who call the shots. These are the nuts and bolts of layer 1 blockchains. They make sure all’s well that ends well, in the high-tech tale of blockchain tech.
Scalability and Security within Layer 1 Ecosystems
Approaches to Enhancing Transaction Throughput
Ever wonder how a layer 1 blockchain stays fast and safe as it grows? Let’s dive in. Primary blockchain layers need ways to handle more deals. We call this need “scalability.” All this means is that the base protocol blockchain must grow without slowing down or crashing.
What’s one way to make this happen? “Sharding” is a big word, but it’s just a method that splits the blockchain into chunks. Each chunk or “shard” runs on its own, which means more deals can happen at once. This makes a layer 1 blockchain work like a busy city with many roads instead of just one.
Another idea is to change the block size. A “block” is like a digital box that holds transactions. If we make the box bigger, we can stuff more transactions into each one. But it’s not just about size; it’s about how often these blocks are made, too. If we can make blocks faster, that’s like the digital boxes traveling on a super-speed conveyor belt.
Proof of work and proof of stake are also part of this story. They’re rules for how deals get added to the blockchain. With proof of work, computers solve hard puzzles to prove they did the work. It’s like showing a ticket before you go on a ride. But this takes much power, time, and money.
Proof of stake, on the other hand, lets people who own more of the cryptocurrency native tokens play a bigger part in the process. Imagine getting extra votes because you own more of the game pieces. It can be faster and greener than proof of work but still needs to be kept in check so that the rich don’t always rule.
Implementing Robust Network Security Measures
Now, how does a basic blockchain stay secure while growing big and fast? Network security is no joke; think of it as the guardians at the gates, the walls around a castle. One key part of this defense is the node validators. These are like watchtowers where volunteer guards watch over the blockchain’s land. They check every deal that happens to make sure it follows the rules—no thieves allowed!
To play it safe, these blockchains use really smart math called cryptography. It scrambles data so only the right person can read it. It’s like writing a secret code on a note that only your best friend can read.
Transaction fees play a role too. No one likes fees, but they help stop spam. It’s like putting a price on throwing trash to keep the place clean. If sending lots of fake deals costs too much, bad guys will think twice.
Lastly, let’s think about finality on blockchain. Finality is when a deal is set in stone, done and dusted. This makes everyone sure that what’s done can’t be undone. Solid finality keeps trust in the system.
So, a layer 1 blockchain has to be a busy bee, working hard on two big jobs: growing big and staying safe. With smart ways to handle more deals and strong security, these digital worlds aim to keep everything smooth and secure, for now and the future.
Exploring Key Layer 1 Blockchain Networks
Ethereum’s Impact and Evolution
Let’s dive into layer one blockchains, using Ethereum as a key example. Ethereum is like a big computer for the world. Anyone use it, build on it, or send value across it. It changed the game. Now, it holds more than money. With it, you can make deals without a middleman. Those deals use smart contracts, big for business and apps.
But Ethereum had speed bumps. It was like a busy highway that needed more lanes. So, the team worked hard to make it better and faster. That means it has new ways to handle more traffic. This helps everyone use Ethereum without a long wait.
Ethereum is special because you can build anything on it. Think of it like Lego: You stack blocks to make new things. With Ethereum, these things are called decentralized apps, or dApps for short. dApps can be games, markets, or even social media. The best part? You’re in control, not a company.
It’s amazing to see how Ethereum grows and changes. It started simple. Now it helps thousands of apps work. That’s a big deal in the tech world.
The Endurance of the Bitcoin Network
Now, let’s look at Bitcoin. It’s the first, the biggest, and many say the best. Bitcoin is all about money over the internet. No banks, no cards, just Bitcoin. It keeps going strong because of its simple job. It’s like digital gold that you can send to anyone, anywhere. And the world values that a lot.
Bitcoin uses something called mining. That’s like a big math contest. People use their computers to solve puzzles. These puzzles help keep Bitcoin safe and working. The prize? New Bitcoins. That’s how Bitcoin grows without a boss.
Even though there are newer coins, Bitcoin is still a star. It’s the one people know and trust the most. And in a world full of change, trust is huge.
Both Ethereum and Bitcoin show different paths for layer one blockchains. One is a platform for the future. The other, a new kind of money. Yet they share something. Both help us think different about trust, value, and working together.
They are like two trees in a forest of tech. They stand tall, showing the power of layer one blockchains. And as they evolve, we can’t wait to see what fruits they bear next. This is the world of base protocol blockchains. They are our digital rock, and the foundation technology we can all build upon.
We dove into the key parts of Layer 1 blockchains. We looked at how these systems work and how they deal with lots of data safely. We saw that smart contracts and native tokens are central for on-chain activities and keeping the network in check. We examined different ways to grow, like boosting transaction speed, and keeping the network tough against attacks.
Every Layer 1 network, like Ethereum and Bitcoin, shows these points in action. Think of them as cities built on strong bases with their own rules and ways to get bigger and stay safe. I hope you now get the nuts and bolts of these blockchain layers. They’re vital for crypto to work well and keep growing. Keep an eye on them – they’re shaping our digital future!
Q&A :
What is a Layer 1 blockchain?
A Layer 1 blockchain is the foundation of a blockchain network, consisting of the main protocol that defines the rules of the network. It’s similar to the operating system of a computer; it’s the base technology that allows for the creation, validation, and recording of transactions on a decentralized ledger. Examples include Bitcoin, Ethereum, and other primary blockchain infrastructures.
How does a Layer 1 blockchain maintain security and consensus?
Layer 1 blockchains maintain security and consensus through various mechanisms such as Proof of Work (PoW), Proof of Stake (PoS), or other consensus algorithms. These mechanisms ensure that all participants in the network agree on the current state of the blockchain and that transactions are confirmed and immutable. This prevents double spending and maintains the integrity of the blockchain.
What differentiates Layer 1 from Layer 2 blockchain solutions?
Layer 1 refers to the underlying main blockchain architecture, while Layer 2 solutions are built on top of Layer 1 blockchains to enhance their scalability and efficiency. Layer 2 solutions, such as the Lightning Network for Bitcoin or rollups for Ethereum, handle transactions off the main chain and later settle them on the main chain, thereby increasing the transaction capacity without compromising the security of the Layer 1 blockchain.
Why is scalability an issue for Layer 1 blockchains, and how are developers addressing it?
Scalability is an issue for many Layer 1 blockchains because they can process only a limited number of transactions per second, which may lead to network congestion and higher fees. Developers address scalability through a variety of methods, including upgrading consensus algorithms (e.g., moving from PoW to PoS), implementing sharding (dividing the network into smaller, more manageable pieces), or through Layer 2 solutions meant to offload transaction volume from the main chain.
Can Layer 1 blockchains interoperate with each other?
Interoperability among Layer 1 blockchains is not inherent and often requires additional protocols or infrastructure to facilitate communication and value transfer between separate blockchain networks. Projects like Polkadot and Cosmos are working on creating an internet of blockchains where different Layer 1 blockchains can interact seamlessly, fostering a more connected and efficient blockchain ecosystem.