In the era of Industry 4.0, blockchain is increasingly playing an important role in finance, investment, and cryptocurrency. However, a new technology is emerging that has the potential to overcome many of the limitations of traditional blockchain: Directed Acyclic Graph (DAG). So, what is DAG Blockchain, and what makes it stand out compared to traditional blockchain? Let’s explore in this article.
What is DAG Blockchain?
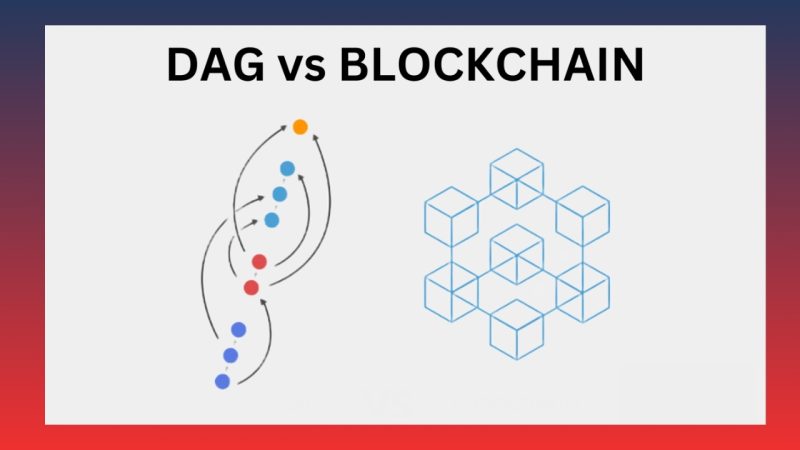
Directed Acyclic Graph (DAG), also known as a directed graph without cycles, is a special data structure used in some blockchain systems to improve scalability and efficiency. Unlike traditional blockchain, where transactions are stored in consecutive blocks, DAG does not use blocks. Instead, transactions are recorded as vertices in the graph. These vertices can link to each other in a directed structure without forming loops, allowing the system to process transactions faster and more energy-efficiently.

How does DAG work?
DAG (Directed Acyclic Graph) works differently from traditional blockchain. Instead of using blocks, DAG uses vertices (points) and edges (connections) to record and verify transactions. The structure of DAG is a directed graph, where transactions (vertices) are connected through directed edges, and there are no cycles, meaning no circular paths exist.
In a DAG system, each new transaction references previous transactions, rather than being grouped into sequential blocks like in blockchain. This allows transactions to be verified simultaneously, improving transaction speed and reducing congestion since there is no dependence on a linear chain.
With DAG, transactions can be processed in parallel, enhancing scalability and saving energy because mining blocks like in traditional blockchain is not required. Transaction validation occurs as soon as a transaction is made, without waiting for confirmations from other blocks.

Comparing DAG Blockchain with traditional Blockchain
Structure and operation
- Traditional Blockchain: Traditional blockchain uses a chain of blocks that contain information about transactions. Each new block is added only after the previous block is verified, resulting in a linear block chain. This creates a dependency on verifying each block, reducing transaction processing speed, especially when the volume of transactions is high.
- DAG Blockchain: In contrast, DAG does not use blocks but employs a directed graph to record transactions. Each new transaction can link to one or more previous transactions, allowing the system to process transactions concurrently without experiencing congestion, as there is no reliance on a linear chain.
Scalability
- Traditional Blockchain: Although blockchain systems like Bitcoin or Ethereum have made improvements to enhance scalability (e.g., Ethereum 2.0), they still face congestion issues when there are too many transactions.
- DAG Blockchain: DAG offers superior scalability over traditional blockchain because transactions can be verified simultaneously. This reduces the load on the system, alleviates congestion, and processes millions of transactions in a short period.
Energy efficiency and transaction costs
- Traditional Blockchain: Traditional blockchains, especially systems like Bitcoin, require an energy-intensive mining process to validate and add new blocks to the chain. This leads to high transaction costs.
DAG Blockchain: Since mining is not used, DAG is far more energy-efficient and has significantly lower transaction costs compared to traditional blockchain.
Practical applications of DAG Blockchain
DAG (Directed Acyclic Graph) is not just a new technology but also opens up many practical applications in fields like cryptocurrency, IoT, finance, and big data. Here are some prominent applications of DAG Blockchain:
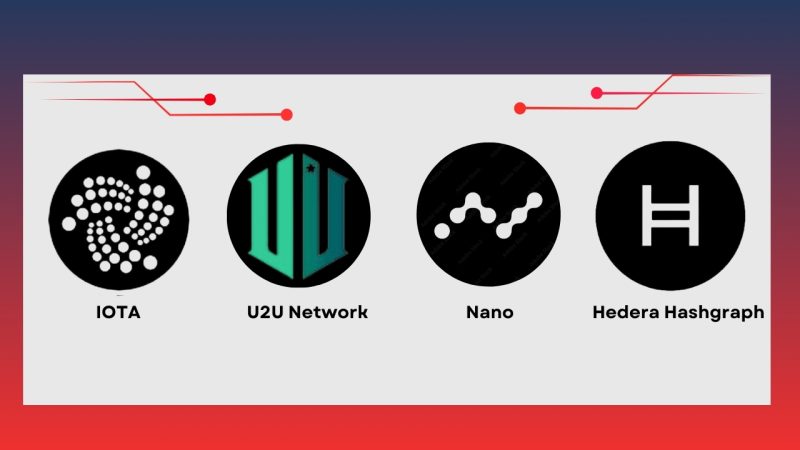
- IOTA: Cryptocurrency for IoT IOTA uses DAG to process transactions in parallel without mining blocks, eliminating transaction fees. This makes IOTA an ideal choice for IoT systems, where millions of devices need to transact quickly and without costs.
- U2U Chain: Combining DAG with ILP Protocol U2U Chain combines DAG with the Interledger Protocol (ILP) to create a decentralized application development platform. This combination enhances scalability, enables connectivity with other blockchain networks, increases interoperability, and reduces transaction latency.
- Nano: Instant Payments with No Fees Nano uses DAG with a “block-lattice” structure, allowing transactions to occur instantly with no fees. This solution is ideal for high-speed financial transactions and money transfers.
- Hedera Hashgraph: Distributed Financial Solution Hedera Hashgraph uses the “gossip about gossip” mechanism combined with DAG to process thousands of transactions per second, enhancing scalability and reducing costs for financial applications like digital securities and smart contracts.
- Constellation: Big Data and IoT Processing Constellation uses DAG to support big data and AI applications, allowing the processing of large data volumes quickly and efficiently. This technology also supports IoT applications, connecting devices in a network to exchange data securely and effectively.
Benefits of DAG Blockchain
- High scalability: By eliminating the use of a blockchain, DAG can process millions of transactions simultaneously without congestion. This makes DAG an optimal solution for applications that require large-scale scalability, such as IoT systems or global financial services.
- Energy efficiency: Since mining is not required, DAG saves a significant amount of energy compared to traditional blockchain. This not only helps reduce costs but also lowers environmental impact.
- Low transaction Fees: One of the major advantages of DAG is its low or almost zero transaction fees, as there are no blocks required to verify transactions, reducing costs for users and businesses.
- Fast transactions: With simultaneous transaction verification and no need to wait for other blocks, DAG enables rapid transactions, minimizing waiting times for users.

Disadvantages and challenges of DAG Blockchain
- Decentralization issues: One of the main challenges with DAG is decentralization. While DAG improves scalability and reduces transaction costs, some DAG-based systems still lack the full decentralization of traditional blockchain, where anyone can participate in the validation process.
- Difficulty in maintaining system stability: Current DAG networks are not as stable and durable as blockchain. Maintaining and controlling a DAG network can be difficult without mechanisms to manage the system effectively.
- Limited widespread adoption: Despite its advantages, the widespread adoption of DAG is still limited. Systems using DAG need to overcome compatibility issues with existing applications and integrate with traditional blockchain networks.
- Security concerns: Although promising, some DAG networks have not been fully tested for security compared to traditional blockchain networks, where security mechanisms have been proven over time.
Hopefully this article has helped you answer the question “What is DAG Blockchain?” DAG Blockchain is a promising technology, with the ability to process transactions quickly, save energy, and lower costs, especially in areas like IoT, micropayments, and financial applications. However, DAG still faces some challenges such as decentralization and security. With the strong development of DAG-based projects, this technology may play a significant role in the future of blockchain and cryptocurrency.
Don’t forget to follow the next articles at Make Millions With Coin to update more information and interesting knowledge every day.