Distributed Ledger Technology Demystified: Blockchain’s Backbone Explained
Ever wonder what is distributed ledger technology in blockchain? It’s the secret sauce that makes digital coins like Bitcoin tick, but it’s not just for the crypto crowd. In this post, we’ll strip away the tech talk and get down to what DLT really does. It’s like a team working together, but instead of people, it’s a bunch of computers. They all share the job of keeping records straight, without letting any single one take over. Think of DLT as a group project where everyone’s on the same page—literally. Let’s dive into the simple truths behind this tech and see why it’s changing the game in ways that matter to you.
Understanding the Basics of Distributed Ledger Technology (DLT)
Defining DLT and Its Role in Blockchain
So what is this thing called DLT? Well, it’s the tech that makes blockchain tick. It’s like a magic book where everyone writes down what they share. But once written, no one can change it. This helps folks trust each other without a middleman.
DLTs are like special databases. But they are not kept in one place. Instead, they are spread across many places. This means that no single person or company has control over all the information.
How does this connect to blockchain? Imagine blockchain as a chain of blocks. Each block is a mini-database. Now link many of these chains, and that’s your blockchain, with DLT as its heart.
Key Features of Distributed Ledgers
First up, DLT lets everyone see the same data at the same time. This is huge because it means everyone can trust the info without doubting. You don’t need to call someone to check if things are correct.
Next, DLT is very tough to mess with. Once you put data in, it’s like it’s set in stone. This keeps our info safe and sound. This is super important when dealing with money or secrets.
Then, we have smart contracts. They are like deals in code. If you do X, you get Y. No need for someone to check if you did X; the code does that. And it runs on DLT.
Lastly, DLT scales well. It’s built to grow. As more people join in, it can handle them. Think of it like a party. At first, a few friends can fit in your living room. But what if the whole town wants to come? With DLT, you move the party to a huge park where everyone fits.
In short, DLT in blockchain is all about sharing info safe and sound, far and wide. It’s seeing the same thing no matter where you are. That’s DLT for you – a pillar of trust in the digital world.
Architectural and Operational Differences: DLT vs Traditional Databases
Centralized versus Decentralized Systems
Imagine a spider web with no center. That’s how DLT systems work. They spread out data across many places. On the other hand, traditional databases are like a treasure chest. All the information is locked up in one spot. When you use DLT, everyone gets a copy of the data. They can all check it and trust it. It’s not like this with centralized databases. There, only one person or group handles all the info.
In simple words, DLT lets lots of computers hold the same records. They work together but no single one controls the records. This way, if one computer has a problem, the records are still safe with others. Unlike traditional databases, where if the one computer with all the info goes down, the data might be at risk.
The Mechanisms of Consensus in DLT
Let’s talk about how all these computers agree on what’s true. This is called consensus in DLT. It’s like if you and your friends have to decide on a game to play. You would talk and come to a choice everyone likes. That’s a bit like how computers in a blockchain make decisions. They use set rules to agree on what the data should be. Everyone follows these rules so they can all trust the records.
These rules or “mechanisms of consensus” make sure that everyone’s copy of the data matches. They help keep the ledger honest and up-to-date. Think about a game where you need to make sure everyone is playing fair. These rules are there to make that happen for blockchain.
Blockchain uses cool systems so all the computers agree without needing one boss. Knowing this can help you see why DLT is so safe. It’s hard to cheat when so many are watching and checking based on the rules. Plus, new records must get the okay from others before they join the blockchain. This keeps the data they share strong against wrong changes.
When we think about how these networks work, it’s a game-changer for keeping data safe. It’s not just about one person or place. It’s about a whole team making sure everything is right. And they do this by always following the rules they all agreed on.
Each computer, or node, has a role to play in this. They check and pass on the data, making sure it’s correct. This teamwork makes DLT strong against attacks. It also makes the data shared see-through, so anyone can check it.
This is the heart of why DLT is important in places like finance, where trust is key. It can show clearly who owns what without a middle man. In supply chains, it can track goods in a way that can’t be faked. This is just the beginning, as DLT is set to change so many parts of how we deal with info and value.
So, by splitting the power among many and using set rules, DLT gives us a new, safe way to keep and share data. This is why so many now see it as the future for anything that needs clear, honest records.
The Building Blocks of DLT and Their Functions
Components and Structure of a Distributed Ledger
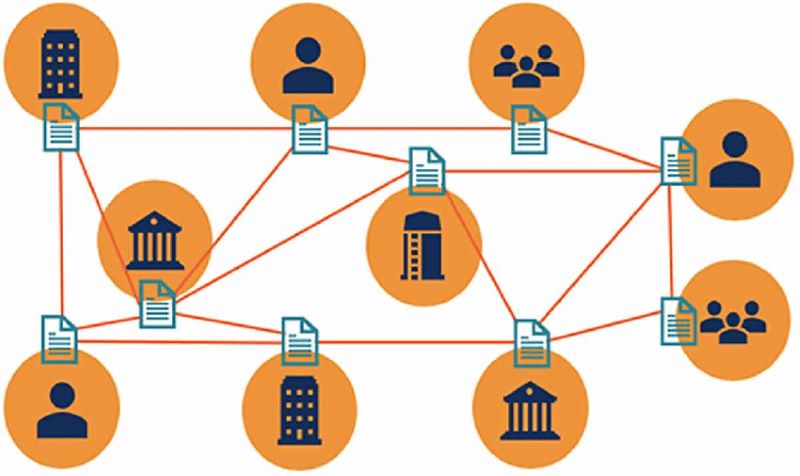
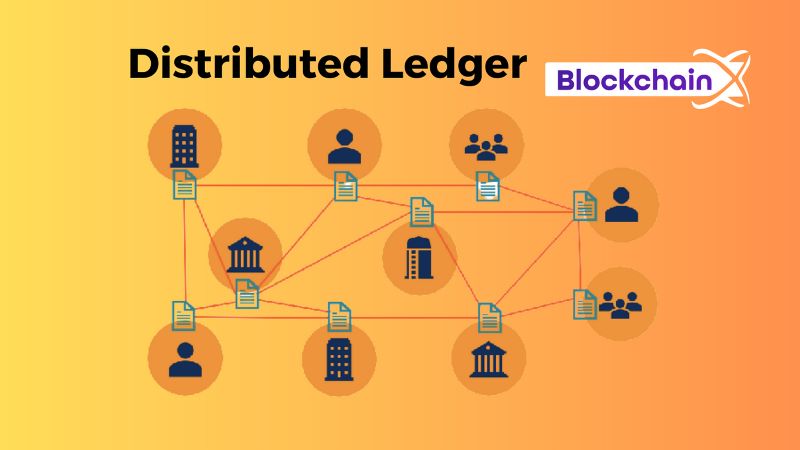
Imagine a world where keeping track of money, property, and even votes is safe and simple. That’s the promise of blockchain, a key player in the digital world. At its heart lies distributed ledger technology (DLT). Let’s break down how DLT works. First, imagine a ledger. This is like the book where your grandma writes down every penny she spends or earns. But, instead of one book, every person has the same copy. Every time there’s a change, everyone’s book updates. That’s distributed ledger technology. You can’t cheat because everyone would know.
DLT systems in blockchain are the guts of the system. They’re made up of three parts: a ledger, nodes, or people and machines that join the network, and transactions, like sending money or signing a contract. With blockchain, these components work together in an exciting way. When someone makes a transaction, everyone on the network checks it. They make sure it’s fair and follows the rules. Then, the change is added to the ledger, linking with past data. This link is the “chain” in blockchain.
One amazing thing about this is everyone sees the same data at the same time. Changes show up for everyone at once. It’s like magic, keeping everything open and honest. Plus, it’s tough to mess with records in blockchain because you’d have to change the data on every computer in the network at the same time. That’s a big part of why DLT is safer than old systems.
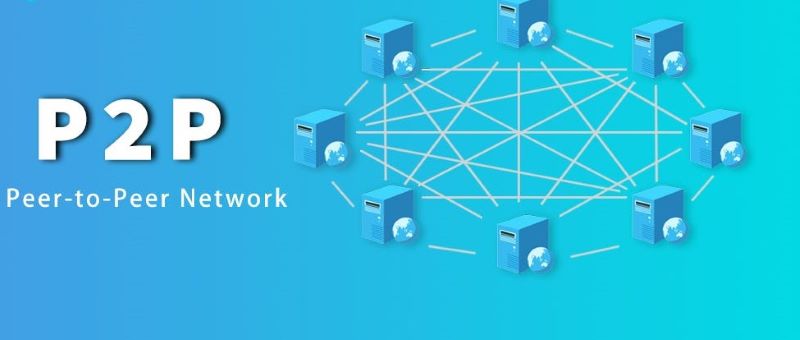
The Significance of Peer-to-Peer Networks in DLT
Now, let’s talk about friends talking to each other. In DLT, we call it peer-to-peer (P2P) networks. Just like kids trade cards directly with each other on the playground, P2P lets computers talk straight to one another. They don’t need to go through a middle person like a bank or a website. This is key for DLT blockchain differences.
Thanks to P2P, sending information or money is faster and cheaper. You might wonder why it’s better. Well, because all the computers on the network work together. It’s like a big team, making sure everything runs smooth and stays safe. This team checks all that happens on DLT, keeping records straight without needing any boss.
In a P2P network, if one computer has a problem, the rest keep going. This makes the whole system stand strong, even if parts have trouble. That’s a huge advantage of distributed ledgers. Plus, it’s not just for tech wizards. Businesses, banks, and even everyday people can use DLT. It can help make things work better for everyone.
Understanding DLT, from how it’s built to how it uses teamwork in networks, is a big deal. It’s changing how we take care of important stuff, from our money to how we do business. It’s cool to see how a simple idea of a shared ledger can do so much. It’s not just for money like Bitcoin; it can be for anything of value. With brains behind it and the trust it builds, DLT is setting up to change the world in good ways.
Real-World Applications and the Future of DLT
DLT’s Impact on Various Sectors
Distributed ledger technology, or DLT, is changing how we do things. It’s like a giant, secure, shared notebook that many can write in, but no one can erase. Think of it as a record of facts or promises that we all can trust, without needing one person in charge of it. This is powerful stuff across many areas – like finance, supply chains, and keeping records safe.
In finance, DLT helps to move money faster and with less risk of mistakes. It’s like having a super-accurate, very fast helper for banks so that when people send money, it goes where it should, quickly. Supply chains also get smarter with DLT. It lets us track things – from fresh apples to the newest phone – all the way from where they start to where they end. This means we can be sure that what we buy is good and came to us the right way.
For keeping records, DLT is like a superhero. It keeps our important info safe from bad guys and can’t be fiddled with. That means things like house deeds or your medical history stay correct and only seen by the right people. The neat thing is that it works for everyone at the same time. So everyone has the same up-to-date records without waiting or worrying.
Now, imagining the future is fun. DLT is not stopping anytime soon. It can make so many things better – voting from our couches, or even getting rid of that stack of papers on our desks. The future looks bright with DLT in it.
Innovations and Trends in Distributed Ledger Technology
Staying ahead in DLT means being on the lookout for new ideas and ways to use it. Smart contracts are a big deal. They’re like robot deal-makers living in the DLT that make sure everyone sticks to their word. No cheating, no forgetting. They just follow the rules and make everything fair. This takes out a lot of waiting and worrying when making deals or selling things.
We’re also seeing more people talk about “Public vs. Private blockchains”. Both are kinds of DLT but work differently. Public ones are open to everyone – like a community garden. Private ones are closed and only for some people – more like a locked diary. Each has its special uses, and knowing which to use and when is key.
Along with this, we have the growth of Blockchain as a Service (BaaS). This is like renting a piece of the DLT for your own project, so you can try out cool ideas without building the whole system yourself. It’s like playing in a sandbox that’s got all the best toys already.
We’re also pushing the limits of how DLT works with other tech like AI. Imagine a smart DLT that makes its own decisions. Scary, but also kind of amazing. This could make things even more secure and handy for all of us.
DLT is here to make things better. It’s fast, it’s fair, and it’s the future. As we keep exploring and trying new things, it’s sure to surprise us with ways to make our world work smoother. Let’s keep our eyes peeled for what comes next in the journey of DLT!
We just explored Distributed Ledger Technology, or DLT. We learned it’s a key part of blockchain and has features unlike typical databases. We saw how it’s different in structure and operation, with a focus on decentralized, peer-to-peer systems.
We dug into how DLT works, its parts, and why peer networks matter. We also looked at how DLT changes things like finance and health care and peered into the future of this tech.
In closing, DLT isn’t just tech talk. It’s a game changer, bridging gaps we never thought possible. Keep your eyes on it; it’s shaping our world right now.
Q&A :
What Exactly Is Distributed Ledger Technology in Blockchain?
Distributed Ledger Technology (DLT) is a digital system for recording the transaction of assets in which the transactions and their details are recorded in multiple places at the same time. Unlike traditional databases, DLT has no central data store or administration functionality. In a blockchain, which is a type of distributed ledger, data is stored in blocks that are then chained together.
How Does Distributed Ledger Technology Work Within Blockchain?
Within a blockchain, distributed ledger technology works by spreading the information across a network of interconnected computers or nodes. Each node has a copy of the ledger and participates in consensus algorithms to agree on ledger updates, which makes it incredibly difficult to alter recorded data without detection. This ensures transparency, security, and immutability of the data recorded on the ledger.
What Advantages Does DLT Offer Over Traditional Databases?
Distributed Ledger Technology offers several advantages over traditional databases, including enhanced security due to its decentralized nature which reduces the risk of hacking or corruption. Transparency is another advantage since all participants have access to the same ledger. Moreover, it eliminates the need for a central authority or third-party verification, which can streamline processes and reduce costs.
Are Blockchain and Distributed Ledger Technology the Same?
While blockchain is a type of distributed ledger technology, not all DLTs are blockchains. Blockchain is a DLT that maintains a growing list of ordered records, called blocks, which are linked using cryptography. However, there are other forms of DLTs like directed acyclic graphs (DAGs) that do not structure their data into blocks or use chains but still distribute transactions across a network for validation.
What Industries Can Benefit From Using Distributed Ledger Technology?
Many industries can benefit from using Distributed Ledger Technology, including finance for secure and transparent transactions, supply chain management for tracking product history, healthcare for safeguarding patient data, voting systems for ensuring election integrity, and many others where secure, transparent, and immutable record-keeping is essential. As this technology matures, its applications are expected to expand even further across various sectors.